Transformer models have revolutionized the field of natural language processing (NLP) and have become the go-to architecture for various tasks, including machine translation, text generation, and sentiment analysis. Since their introduction, several advancements have been made in transformer model development, enhancing their performance and expanding their applications. In this article, we will explore seven significant developments in transformer models.
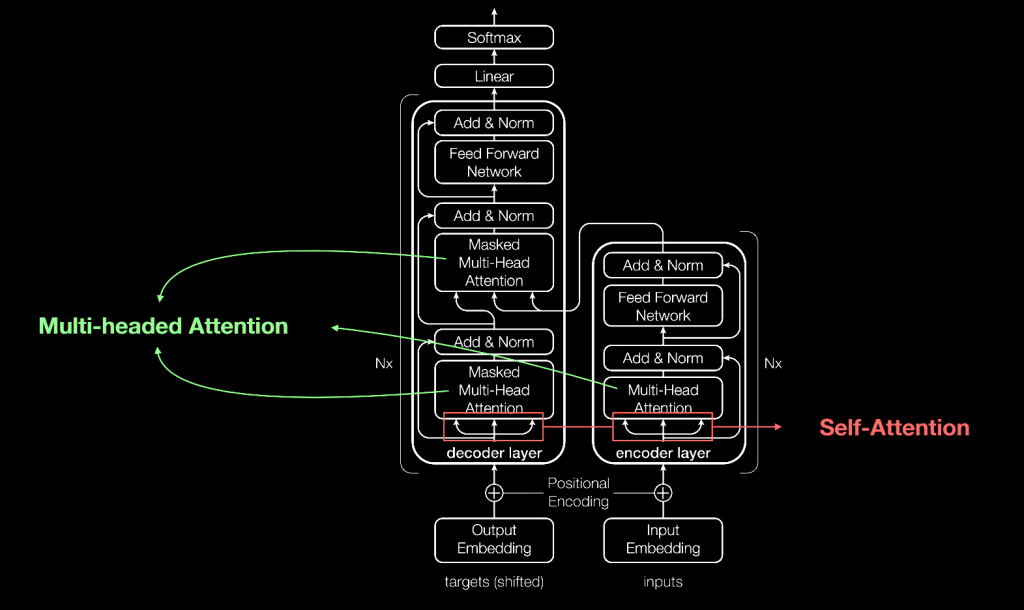
- BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers): Introduced in 2018, BERT brought a breakthrough in NLP by pre-training a transformer model on large amounts of unlabeled text data. BERT’s bidirectional approach enabled it to capture the contextual information of a word by considering both its preceding and succeeding words. This development significantly improved the accuracy of various NLP tasks.
- GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer): GPT, developed by OpenAI, focused on leveraging the transformer architecture for text generation. The model was trained on massive amounts of internet text data, enabling it to generate coherent and contextually relevant text. GPT revolutionized the field of language generation, leading to advancements in chatbots, automated content creation, and creative writing assistance.
- Transformer-XL: Traditional transformer models suffer from a limitation in handling long-range dependencies due to their fixed-length context window. Transformer-XL addressed this issue by introducing recurrence within the transformer architecture. This allowed the model to remember past information and handle longer contexts, resulting in improved performance for tasks involving longer sequences, such as document understanding and language modeling.
- T5 (Text-to-Text Transfer Transformer): T5 introduced a unified framework for various NLP tasks, including classification, translation, summarization, and question-answering. Instead of developing task-specific models, T5 trained a single model capable of performing multiple tasks. This approach simplified the development process and made it easier to transfer knowledge across different tasks.
- BigBird: Traditional transformer models have a quadratic dependency on the sequence length, making them computationally expensive for longer sequences. BigBird addressed this limitation by introducing sparse attention mechanisms that scale linearly with the sequence length. This development made it feasible to process longer sequences efficiently, benefiting tasks such as document classification, document understanding, and genome analysis.
- Reformer: Reformer focused on optimizing the transformer architecture by introducing locality-sensitive hashing and reversible computing. These techniques reduced the memory requirements of the model without compromising its performance. The Reformer model enabled training on longer sequences while using less computational resources, making it more accessible for practical applications.
- DeiT (Data-efficient image Transformers): While transformers were initially designed for text-based tasks, DeiT expanded their applications to computer vision. DeiT demonstrated that transformer models can achieve state-of-the-art performance on image classification tasks with significantly fewer training samples than traditional convolutional neural networks. This development opened up new possibilities for using transformers in various image-related applications.
In conclusion, transformer models have witnessed significant advancements since their inception. From BERT’s contextual understanding to GPT’s text generation capabilities, these developments have propelled the field of NLP forward. The introduction of models like T5 and DeiT has expanded the scope of transformers beyond text, making them a versatile choice for a wide range of tasks. With ongoing research and development, transformer models are likely to continue evolving and shaping the future of artificial intelligence.
To learn More:- https://www.leewayhertz.com/transformer-model-development-services/