Image synthesis refers to the process of generating new images that do not exist in the real world, often based on existing datasets or models. Generative AI models, such as Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Variational Autoencoders (VAEs), have gained significant popularity in recent years for their ability to create realistic and diverse images. If you’re interested in building generative AI models for image synthesis, here are some key points to consider:
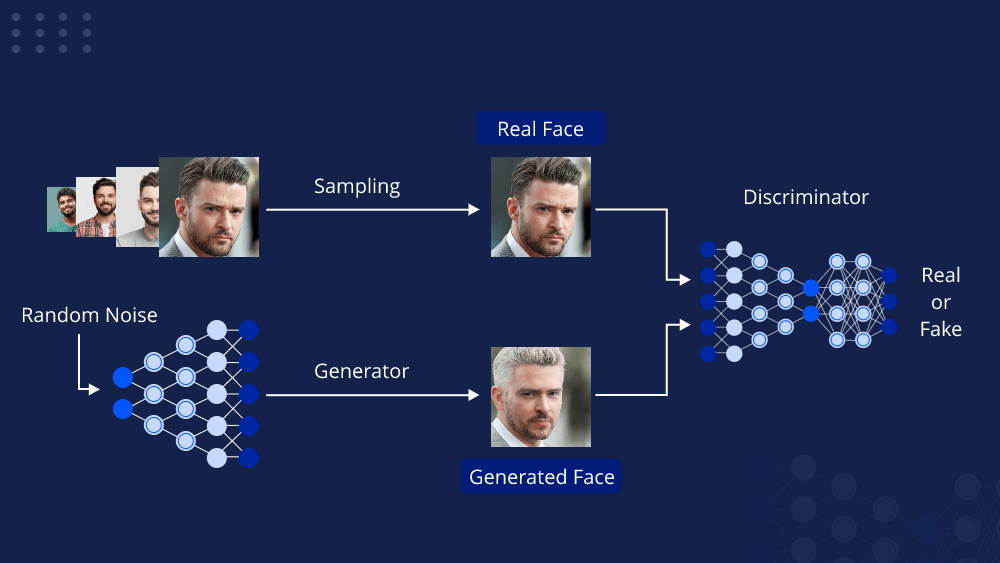
1. Understand the Basics:
- Familiarize yourself with the fundamental concepts of generative AI, including GANs and VAEs. GANs consist of a generator network that creates images and a discriminator network that tries to distinguish between real and generated images. VAEs use an encoder-decoder architecture to learn a latent representation of images.
2. Gather and Preprocess Data:
- Acquire a dataset that aligns with your desired image synthesis task. Ensure that the dataset contains a diverse range of images and covers the target domain adequately.
- Preprocess the data by resizing, cropping, normalizing, and augmenting the images as needed. This step helps improve the model’s generalization and performance.
3. Select an Appropriate Architecture:
- Depending on your project requirements, choose the most suitable generative model architecture. GANs and VAEs have different characteristics and strengths, so consider their respective advantages and limitations.
- Experiment with different variations and modifications of the base architectures to enhance performance, stability, or specific image synthesis objectives.
4. Train the Model:
- Split your dataset into training and validation sets. The validation set helps monitor the model’s progress and avoid overfitting.
- Train the generative model using an appropriate loss function, such as binary cross-entropy for GANs or a combination of reconstruction loss and regularization terms for VAEs.
- Iterate the training process, adjusting hyperparameters and monitoring performance until the model converges to a satisfactory result.
5. Evaluate and Fine-Tune:
- Assess the quality of the generated images by conducting both qualitative and quantitative evaluations. Qualitative evaluation involves visual inspection, while quantitative metrics like Inception Score or Fréchet Inception Distance (FID) provide objective measures.
- Fine-tune the model based on the evaluation results. Adjust hyperparameters, tweak the architecture, or collect additional data if necessary to improve the model’s performance and address any identified limitations.
6. Regularize and Control Outputs:
- Apply regularization techniques to control the diversity, style, or other desired aspects of the generated images. Techniques like adding noise, using latent space interpolations, or incorporating style transfer methods can help shape the output according to specific requirements.
- Explore techniques like conditional GANs, where additional information or constraints can be provided to guide the image synthesis process.
7. Deploy and Iterate:
- Once satisfied with the model’s performance, deploy it for generating new images. Consider the computational requirements and scalability of the model when deploying it in production.
- Continue iterating on the model and data as new insights or requirements emerge. Feedback from users and further analysis can help refine and enhance the image synthesis capabilities.
Building generative AI models for image synthesis is a fascinating and rapidly evolving field. It requires a blend of theoretical understanding, practical implementation skills, and a creative mindset. By following these points and continually exploring new techniques, you can develop powerful generative models that push the boundaries of image synthesis.
To Learn More:- https://www.leewayhertz.com/a-guide-on-generative-ai-models-for-image-synthesis/