Transformers have revolutionized the field of natural language processing (NLP) and have found applications in various domains such as language translation, text generation, and sentiment analysis. They are powerful models based on the attention mechanism that can capture long-range dependencies in sequential data. One recent advancement in transformer-based models is the Decision Transformer, which goes beyond traditional tasks and introduces a novel approach to handling decision-making processes. In this article, we will explore how to use the Decision Transformer in a transformer-based model.
Understanding the Decision Transformer:
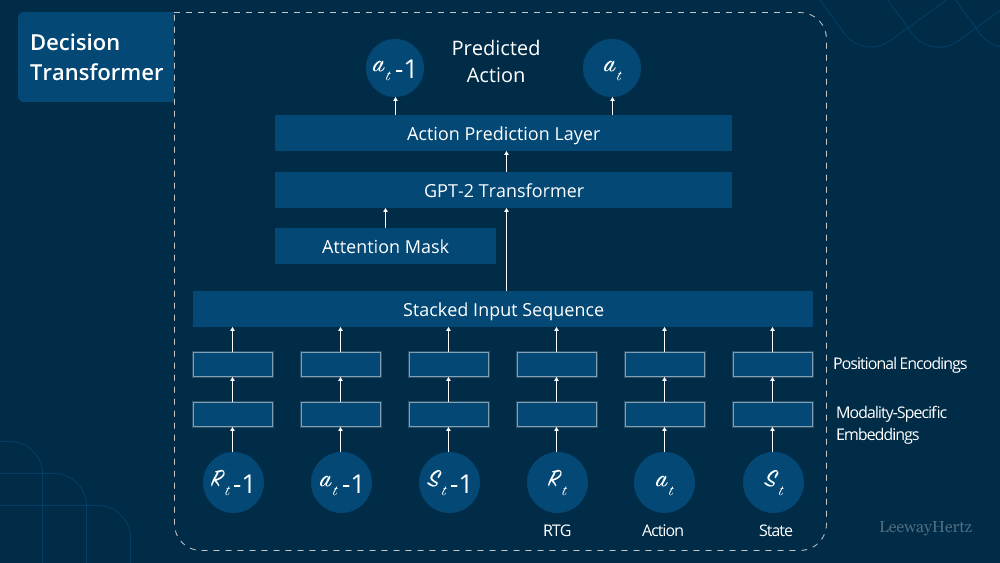
The Decision Transformer is an extension of the traditional transformer architecture, which incorporates decision-making capabilities into the model. It was introduced to address problems where sequential data is intertwined with decisions at various stages. Such tasks could include chat-based dialogue systems, recommendation systems, and interactive game-playing agents.
The Decision Transformer introduces two main components: the decision block and the decision pointer. The decision block is responsible for encoding the decision context, while the decision pointer is utilized to select the appropriate decision at each decision-making step.
Step 1: Data Preparation:
As with any machine learning task, data preparation is a crucial step. The decision-making task should be formulated in such a way that the input sequence incorporates both the raw sequential data and the decision context. Additionally, the decision options must be defined for each decision point in the data.
Step 2: Model Architecture:
To utilize the Decision Transformer, we need to modify the standard transformer architecture slightly. Specifically, we must incorporate the decision block and the decision pointer into the model. The decision block can be added as an additional layer in the encoder to process the decision context, while the decision pointer is a learnable parameter that is utilized to select the decision at each decision-making step.
Step 3: Input Encoding:
During the input encoding step, we prepare the data to be fed into the Decision Transformer. The sequential data is encoded in the same way as in a traditional transformer. However, for the decision context, we may represent it as a separate embedding or append it to the input sequence with special tokens to distinguish it from the raw data.
Step 4: Decision Context Processing:
In the decision block, the decision context is processed to capture the relevant information for decision-making. This could involve passing the context through a series of feed-forward layers or employing a self-attention mechanism to extract relevant features.
Step 5: Decision Pointer:
The decision pointer is a crucial component that determines the decision to be made at each step. It takes into account the encoded decision context and generates a probability distribution over the available decision options. The decision with the highest probability is then selected.
Step 6: Training:
During the training process, the model is optimized to make accurate decisions based on the input sequence and the decision context. The model’s parameters, including the decision pointer, are updated using backpropagation and an appropriate loss function.
Step 7: Inference:
Once the Decision Transformer is trained, it can be used for making decisions on new input sequences. During inference, the model follows the same process as during training, but instead of updating parameters, it utilizes the learned weights to make decisions based on the given input and decision context.
Conclusion:
The Decision Transformer is a promising extension of the traditional transformer architecture that enables models to perform decision-making tasks alongside sequential data processing. By incorporating decision blocks and decision pointers, the model can effectively make decisions based on the input sequence and the provided decision context. As the field of NLP continues to advance, the Decision Transformer opens up new possibilities for interactive and dynamic applications, ranging from chatbots with decision-making capabilities to personalized recommendation systems. With further research and development, the Decision Transformer is likely to play a vital role in enhancing the capabilities of transformer-based models in the future.
To Learn More:- https://www.leewayhertz.com/decision-transformer/