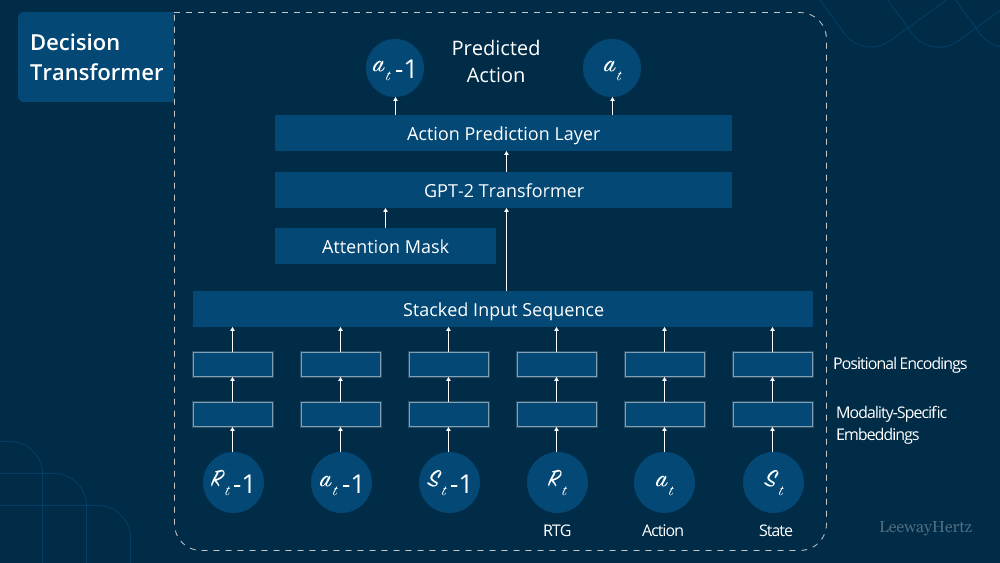
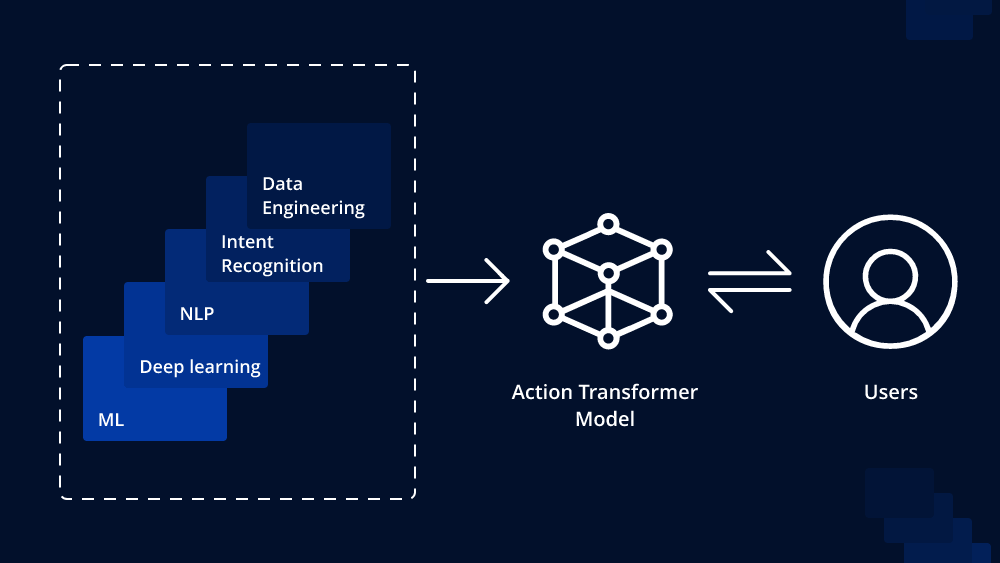
In recent years, the rapid advancements in artificial intelligence and natural language processing have given rise to a new generation of chatbots that go beyond simple text-based interactions. Among these innovative chatbots, transactional chatbots have emerged as powerful tools that facilitate seamless, automated transactions between users and businesses. From customer support to e-commerce, these intelligent virtual assistants are revolutionizing the way we engage and transact online. In this article, we will explore what transactional chatbots are and delve into their operational mechanisms.
Understanding Transactional Chatbots:
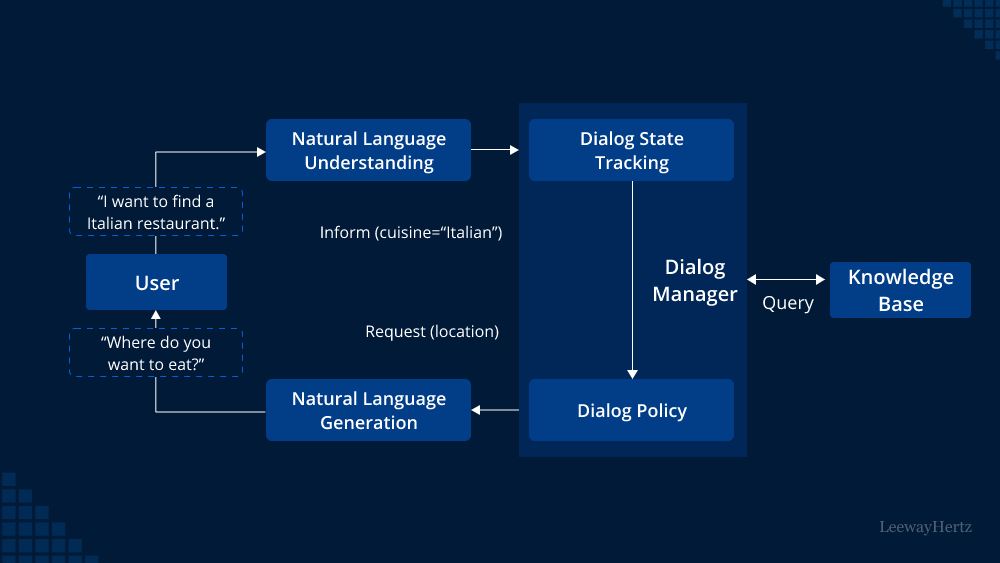
A transactional chatbot is an advanced conversational AI system designed to facilitate and execute specific actions or transactions within a chat interface. Unlike traditional chatbots that provide pre-programmed responses, transactional chatbots leverage machine learning algorithms to understand natural language and context, enabling them to handle complex tasks. These tasks may include processing orders, making reservations, providing personalized recommendations, handling payments, and more.
Operational Mechanisms:
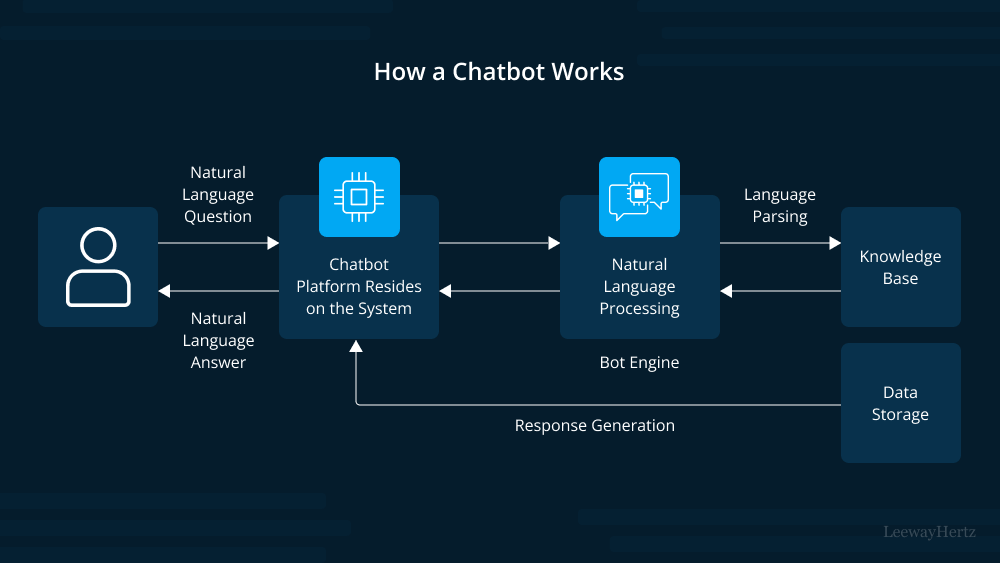
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): The core technology that drives transactional chatbots is natural language processing (NLP). NLP allows chatbots to understand and interpret human language in a way that traditional rule-based chatbots cannot. By analyzing the user’s input, NLP enables the chatbot to extract the user’s intent and context accurately.
- Intent Recognition: Transactional chatbots utilize intent recognition techniques to identify the user’s intent behind their message. Whether a user wants to make a purchase, book a flight, or inquire about a service, the chatbot aims to grasp the user’s intention to respond accurately.
- Context Awareness: A key feature of transactional chatbots is their ability to maintain context throughout the conversation. This means that the chatbot can remember past interactions within the same session, allowing for a more personalized and efficient transactional experience.
- Integration with Backend Systems: To execute transactions, transactional chatbots are integrated with backend systems or databases. For example, an e-commerce chatbot may connect with the inventory and payment systems of an online store. This integration enables the chatbot to access real-time data and process transactions seamlessly.
- Authentication and Security: As transactional chatbots handle sensitive information like payment details, security is paramount. These chatbots employ various authentication methods to verify user identities and ensure secure transactions, such as two-factor authentication or biometric verification.
- Personalization: Transactional chatbots often incorporate user data and preferences to provide personalized recommendations and offers. By analyzing past interactions and purchase history, the chatbot can offer more relevant and tailored suggestions to users.
- Fallback Mechanism: While transactional chatbots are highly advanced, they may not always understand every user query. In such cases, they employ a fallback mechanism, where they either ask for clarification or escalate the conversation to a human agent.
- Feedback and Continuous Improvement: Transactional chatbots gather valuable feedback from users to improve their performance continuously. This feedback loop helps chatbot developers refine the AI model, enhance the user experience, and minimize errors over time.
Benefits of Transactional Chatbots:
- 24/7 Availability: Transactional chatbots operate round the clock, allowing businesses to provide uninterrupted service to their customers.
- Improved Efficiency: By automating transactions, chatbots reduce the need for manual intervention, resulting in quicker and more efficient processes.
- Cost Savings: With fewer resources required for customer support and order processing, businesses can save on operational costs.
- Enhanced User Experience: Transactional chatbots offer personalized interactions, leading to a more satisfying user experience and increased customer loyalty.
- Scalability: Chatbots can handle multiple interactions simultaneously, making them scalable to accommodate growing user demands.
Conclusion:
Transactional chatbots represent a significant leap in the capabilities of conversational AI. Through the power of natural language processing, integration with backend systems, and context awareness, they can execute complex tasks and transactions seamlessly. With continuous advancements in AI technology, we can expect transactional chatbots to play an increasingly vital role in various industries, redefining the way we interact with businesses and making transactions more effortless and efficient than ever before.
To Learn More:- https://www.leewayhertz.com/train-transactional-chatbot-using-reinforcement-learning/